mirror of
https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes.git
synced 2025-06-03 03:59:37 +00:00
- removed image building screens - used DFL setup - used k8s 1.17, OPAE 1.4 and crio 1.16.1 - added bitstream storage screen
140 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
140 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
# Intel Device Plugin Demo for Kubernetes
|
|
|
|
## Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
- [Demo overview](#demo-overview)
|
|
- [Intel® GPU Device Plugin demo video](#intel-gpu-device-plugin-demo-video)
|
|
- [Intel® FPGA Device Plugin demo video](#intel-fpga-device-plugin-demo-video)
|
|
- [Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin OpenSSL demo video](#intel-quickassist-technology-device-plugin-openssl-demo-video)
|
|
- [Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin with DPDK demo video](#intel-quickassist-technology-device-plugin-with-dpdk-demo-video)
|
|
|
|
## Demo overview
|
|
|
|
Acceleration of compute and data processing of workloads like video
|
|
transcoding, compression, and encryption is enabled in Kubernetes with
|
|
the [Device Plugin Framework](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/extend-kubernetes/compute-storage-net/device-plugins/). This repository
|
|
contains a set of Kubernetes plugins and instructions to enable Intel devices
|
|
for the acceleration of your workloads orchestrated by Kubernetes.
|
|
|
|
The current list of supported Intel Device Plugins includes:
|
|
|
|
- [GPU Device Plugin](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/gpu_plugin/README.md) with support for [Intel® Graphics Technology](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/visual-technology/graphics-overview.html)
|
|
- [Intel® FPGA Device Plugin](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/fpga_plugin/README.md)
|
|
- [Intel® QuickAssist Technology (QAT) Device Plugin](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/qat_plugin/README.md)
|
|
|
|
We have included an example demo and configuration information for the Intel
|
|
Device Plugins for Kubernetes below. Please join us on the sig-node-rtk channel
|
|
on [kubernetes.slack.com](https://kubernetes.slack.com/) to ask questions,
|
|
contribute to the community, and learn about the work we are doing with
|
|
Kubernetes and the Device Plugin Framework.
|
|
|
|
## Intel® GPU Device Plugin demo video
|
|
|
|
The screencast demonstrates the deployment of the Intel® GPU Device Plugin for
|
|
Kubernetes including Kubeless Function as a Service (FaaS) media transcoder
|
|
JavaScript function. The media transcoding workload is scheduled on two different worker nodes.
|
|
Only one worker node has a GPU. The time difference in transcoding speed is captured.
|
|
|
|
### Demo platform configuration
|
|
|
|
- Hardware 2-nodes
|
|
- 1x Virtual Machine on Intel® Xeon® E5-2687 CPU @ 3.0 GHz
|
|
- 1x Intel® NUC KIT NUC6i7KYK (Skull Canyon) with Intel integrated GPU
|
|
- Software
|
|
- Ubuntu* 18.04 (Kernel: 4.15.0-36-generic)
|
|
- Kubernetes* 1.11
|
|
- Docker* 18.3.1
|
|
- Intel® GPU Device Plugin built from master branch
|
|
|
|
### Screencast
|
|
|
|
[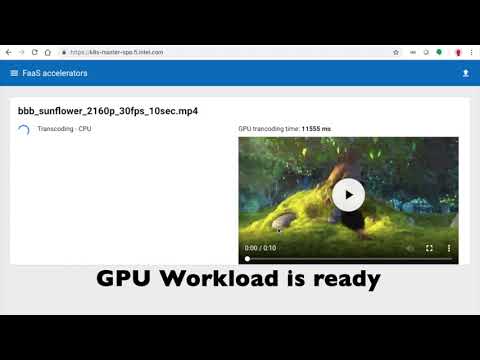](https://youtu.be/sg31rV1FdQk)
|
|
|
|
## Intel® FPGA Device Plugin demo video
|
|
|
|
The screencast demonstrates the deployment of the Intel® FPGA Device Plugin for
|
|
Kubernetes and executes a native loopback 3 (NLB3) workload. The demo begins
|
|
with a fully [configured Kubernetes cluster](https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/independent/create-cluster-kubeadm/)
|
|
with the [Go runtime](https://golang.org/doc/install).
|
|
|
|
### Demo platform configuration
|
|
|
|
- Hardware
|
|
- 1-node, 2x Intel@ Xeon@ Gold 6140M CPU @ 2.30GHz
|
|
- Total memory 377 GB
|
|
- Intel® Arria® 10 GX FPGA
|
|
- Software
|
|
- Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS (Kernel: 4.15.0-60-generic)
|
|
- Kubernetes* 1.13
|
|
- CRI-O 1.13.1
|
|
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin built from master branch
|
|
|
|
### Demo steps
|
|
|
|
1. Validate the status of the [Kubernetes cluster](https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/independent/create-cluster-kubeadm/).
|
|
2. Clone the [Intel Device Plugins for Kubernetes source](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes).
|
|
3. Provision the [admission controller webhook](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/fpga_admissionwebhook/README.md).
|
|
4. Provision the [Intel® FPGA Device Plugin](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/fpga_plugin/README.md).
|
|
5. Build the opae-nlb-demo image
|
|
6. Run the NLB3 workload.
|
|
|
|
### Screencast
|
|
|
|
Intel® FPGA Device Plugin deployment
|
|
|
|
[](https://asciinema.org/a/JuYzNxx9n0eQ1vQBzy86GYBki)
|
|
|
|
## Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin OpenSSL demo video
|
|
|
|
The screencast demonstrates the deployment of the [Intel® QAT Device Plugin](https://github.com/intel/intel-device-plugins-for-kubernetes/blob/master/cmd/qat_plugin/README.md) for
|
|
Kubernetes and executes a sample QAT accelerated OpenSSL workload with the OCI
|
|
compatible Kata Containers runtime, a lightweight Virtual Machine (VM) that feels
|
|
and performs like traditional containers, but provides the workload isolation
|
|
and security advantages of VMs. The demo begins with a fully [configured Kubernetes cluster](https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/independent/create-cluster-kubeadm/)
|
|
and [Kata Containers](https://github.com/kata-containers/documentation/tree/master/install) runtime for workloads.
|
|
|
|
### Demo platform configuration
|
|
|
|
- Hardware
|
|
- 1-node, 2x Intel® Xeon® CPU E5-2687W v4 @ 3.00GHz
|
|
- Total memory 251 GB DDR4
|
|
- Intel® QAT C62x chipset
|
|
- Software
|
|
- OpenSUSE* 15 (Kernel:4.12.14-lp150.12.22-default)
|
|
- Kubernetes* 1.12
|
|
- Containerd 1.2
|
|
- Kata Containers* 1.3.0
|
|
- Intel® QAT Device Plugin built from master
|
|
- QAT 1.7 L.4.3.0-00033
|
|
|
|
### Demo steps
|
|
|
|
1. Load the host drivers and prepare the virtual function (VF) devices.
|
|
2. Check the Kubernetes cluster is in good shape.
|
|
3. Deploy the Intel® QAT device plugin for Kubernetes.
|
|
4. Deploy an Intel® QAT Accelerated OpenSSL workload.
|
|
5. Testing!
|
|
|
|
### Screencast
|
|
Intel® QAT Device Plugin deployment
|
|
|
|
[](https://asciinema.org/a/2N7wF3c9oeCuB9sFqTNm2gmOr)
|
|
|
|
## Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin with DPDK demo video
|
|
|
|
### Demo steps
|
|
|
|
1. Check health of Kubernetes nodes.
|
|
2. Check for allocatable resources.
|
|
3. List QAT Virtual Functions.
|
|
4. Deploy QAT Device Plugin as a Daemonset.
|
|
5. Check again for allocatable resources.
|
|
6. List QAT Virtual Functions again, ensuring they are now bound to DPDK driver.
|
|
7. View pod specification file for pod requesting QAT VFs.
|
|
8. Create pod requesting QAT VFs.
|
|
9. Get a shell to the running container and run a DPDK application.
|
|
|
|
### Screencast
|
|
Intel® QAT Device Plugin with DPDK
|
|
[](https://asciinema.org/a/PoWOz4q2lX4AF4K9A2AV1RtSA)
|